React顶层API
组件
React.Component
React.Component 是使用 ES6 classes 方式定义 React 组件的基类:
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>;
}
}
React.PureComponent
React.PureComponent 与 React.Component 很相似。两者的区别在于 React.Component 并未实现 shouldComponentUpdate(),而 React.PureComponent 中以浅层对比 prop 和 state 的方式来实现了该函数。
如果赋予 React 组件相同的 props 和 state,render() 函数会渲染相同的内容,那么在某些情况下使用 React.PureComponent 可提高性能。
React.PureComponent 中的 shouldComponentUpdate() 仅作对象的浅层比较。如果对象中包含复杂的数据结构,则有可能因为无法检查深层的差别,产生错误的比对结果。仅在你的 props 和 state 较为简单时,才使用 React.PureComponent,或者在深层数据结构发生变化时调用 forceUpdate() 来确保组件被正确地更新。你也可以考虑使用 immutable 对象加速嵌套数据的比较。
此外,React.PureComponent 中的 shouldComponentUpdate() 将跳过所有子组件树的 prop 更新。因此,请确保所有子组件也都是“纯”的组件。
React.memo
创建元素
React.createElement
JSX实际上是React.createElement的语法糖,最终都会转换为React.createElement函数
参考通过源码学习React.createElement
转换元素
React.Children
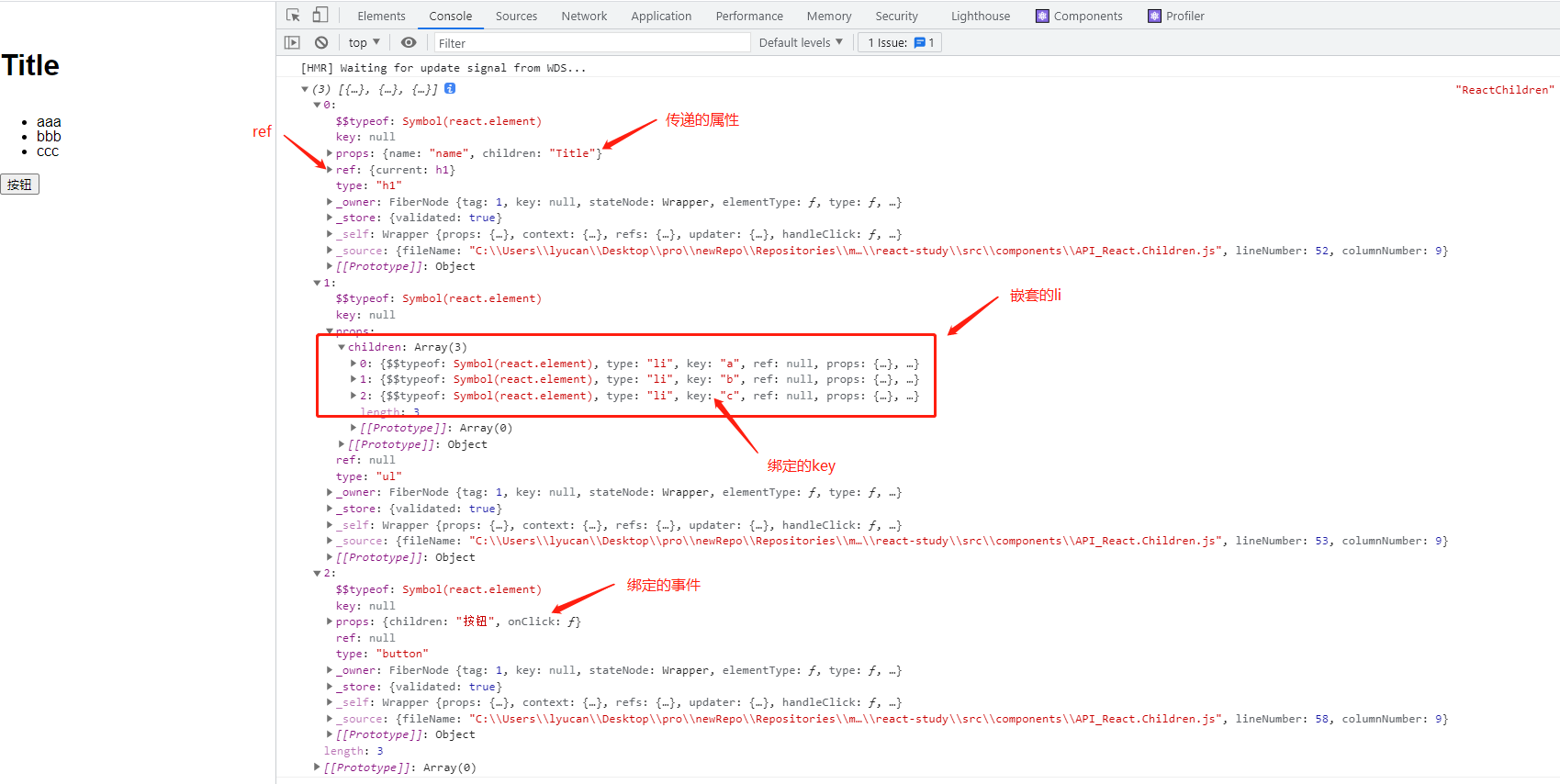
React.Children 提供了用于处理 this.props.children 不透明数据结构的实用方法。
我们先来看看children上有哪些东西
import React from 'react'
class ReactChildren extends React.Component {
render () {
// children还可以是一个函数,如果内部不调用,则会报错,所以内部需要使用this.props.children()来调用
console.log(this.props.children, 'ReactChildren');
return (
<div>
{ this.props.children }
</div>
)
}
}
export default class Wrapper extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.titleRef = React.createRef();
}
handleClick = () => {
console.log('clicked!')
}
render () {
return (
<ReactChildren>
{/* 在children里传入一个函数,内部需要进行调用,否则报错,同样可以进行传参,和render props一样,只不过是写在了children里面 */}
{/* {(msg) => { return <h1>{msg}</h1> }} */}
<h1 name="name" ref={this.titleRef}>Title</h1>
<ul>
<li key="a">aaa</li>
<li key="b">bbb</li>
<li key="c">ccc</li>
</ul>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>按钮</button>
</ReactChildren>
)
}
}
React.Children.map
React.Children.map的实现比数组的map实现要多,因为children的值可能是null,或者其他,直接使用this.props.children.map可能会报错
React.Children.map(this.props.children, (child, index) => {console.log(child, index)})
React.Children.forEach
与 React.Children.map() 类似,但它不会返回一个数组。
React.Children.forEach(this.props.children, (child, index) => {console.log(child, index)})
React.Children.count
输出children的长度
React.Children.count(this.props.children)
React.Children.only
验证 children 是否只有一个子节点(一个 React 元素),如果有则返回它,否则此方法会抛出错误
注意:
React.Children.only()不接受React.Children.map()的返回值,因为它是一个数组而并不是React元素。
try {
console.log(React.Children.only(this.props.children))
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
React.Children.toArray
将 children 这个复杂的数据结构以数组的方式扁平展开并返回,并为每个子节点分配一个 key。当你想要在渲染函数中操作子节点的集合时,它会非常实用,特别是当你想要在向下传递 this.props.children 之前对内容重新排序或获取子集时。
React.Children.toArray(this.props.children)
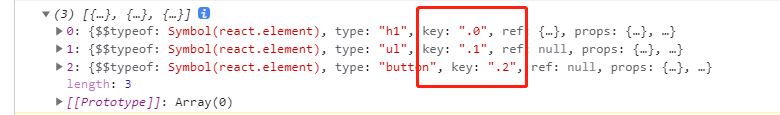
以上所有的方法都不涉及子元素的情况,只能操作当前层级的元素,如果需要操作整个树,需要自己递归。
cloneElement()
cloneElement()是createFactory()的替代品,createFactory()已被废弃
cloneElement()以 element 元素为样板克隆并返回新的 React 元素。返回元素的 props 是将新的 props 与原始元素的 props 浅层合并后的结果。新的子元素将取代现有的子元素(如果子元素里有children,要记得同时传入),而来自原始元素的 key 和 ref 将被保留。
children是只读的,我们不能直接对children进行修改,就可以借助此api进行修改;
{ React.Children.map(this.props.children, (child, index) => {
console.log(child);
return React.cloneElement(child, { style: { color: 'red' }, aaa: 'title' }, [...child.props.children, <span key={null}>新添加的内容</span>])
}) }
类似createElement,第一个参数是具体React元素,第二个参数是扩展的属性,第三个参数是子元素
扩展的属性会进行一个浅合并,相同的属性名将直接覆盖,不相同的则逐个添加到props
子元素是个数组,
- 如果不传,则里面的元素不会发生变化,有多少克隆多少
- 如果传了,则里面的元素会整体替换为传入的元素,因此如果当前元素里面仍存在
children不想丢失,也需要进行扩展
isValidElement()
验证对象是否为 React 元素,返回值为 true 或 false
React.isValidElement(this.props.children)
有一点需要注意的是,判断的元素必须有单一根元素(Fragment也算),像上面例子那种没有单一根元素的,其实是一个数组,都会被判定为false
Fragments
React 中的一个常见模式是一个组件返回多个元素。Fragments 允许你将子列表分组,而无需向 DOM 添加额外节点。
例如在特定标签中(例如table th td),限定标签类型,此时如果有多个标签,给定额外的根标签会使HTML无效,Fragments就解决了此问题
可以使用<React.Fragment>组件,或者短语发<></>
使用显式 <React.Fragment> 语法声明的片段可能具有 key,key 是唯一可以传递给 Fragment 的属性。未来可能会添加对其他属性的支持,例如事件。
Refs
refs相关操作,查阅React ref的使用,或官方文档Refs & DOM/Refs 转发
Suspense
Suspense用于懒加载组件时进行,React.Suspense 可以指定加载指示器(loading indicator),以防其组件树中的某些子组件尚未具备渲染条件。目前,懒加载组件是 <React.Suspense> 支持的唯一用例
import React, { Suspense } from 'react'
const List = React.lazy(() => import('./列表渲染'))
class LazyLoadTest extends React.Component {
render () {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading</div>}>
<List></List>
</Suspense>
)
}
}
export default LazyLoadTest
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 289211569@qq.com